Docker Engine Architecture
Table of contents
Docker is a widely used containerization technology that allows developers to package applications into isolated containers. The Docker engine is the core component of the Docker architecture that makes containerization possible. In this blog, we'll explore the architecture of the Docker engine and how it works.
The Docker engine is made up of several components, including the Docker daemon, containerd, and runc.
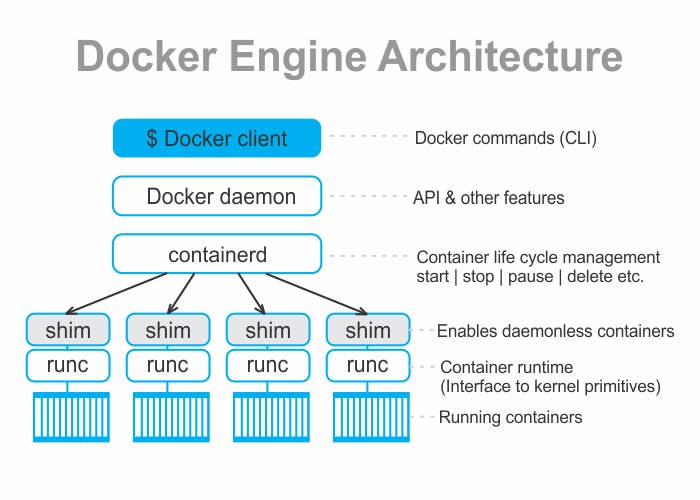
Docker Daemon : The Docker daemon is the primary component of the Docker engine. It runs on the host machine and is responsible for managing the Docker containers, images, and networks. The Docker daemon listens for requests from the Docker client and performs the requested actions. It also interacts with containerd and runc to create and manage containers.
Containerd : It is a container runtime that provides a high-level API for managing containers. It is responsible for low-level container operations, such as container start, stop, and pause. Containerd communicates with the Docker daemon to create and manage containers.
Runc: Runc is a lightweight command-line tool for running containers. It is responsible for setting up the container's environment, creating and managing namespaces, and starting the container process. Runc is used by containerd to start and manage containers.
Runc is a cli tool for spawning and running containers according to OCI specifications(open container specifications).
Containerd-shim : The Containerd-shim is a lightweight process that acts as an intermediary between the Docker daemon and containerd. It is responsible for managing the container's lifecycle and communicating with the Docker daemon.

Docker API : The Docker API is a RESTful API that allows developers to interact with the Docker daemon. It provides a set of endpoints that can be used to perform actions such as creating, starting, and stopping containers. The Docker API is used by the Docker client to communicate with the Docker daemon.
Docker CLI : The Docker CLI is a command-line tool that allows developers to interact with the Docker engine. It sends requests to the Docker API to create, start, and manage containers.
The Docker engine architecture is designed to be modular and flexible. It allows developers to swap out components as needed to suit their specific requirements. For example, developers can replace the container runtime with a different runtime if they prefer.
Some Confusion may occur :
Difference between the working of Containerd and Runc .
Here comes definitions of low-level runtimes and high-level runtime.
Actual container runtimes that focus on just running containers are usually referred to as “low-level container runtimes”. Low-level runtimes support using these operating system features[namespaces and cgroups].
Runtimes that support more high-level features, like image management and gRPC/Web APIs, are usually referred to as “high-level container runtimes” or usually just “container runtimes”.
Finally:
Containerd is a (high-level) container runtime, as it manages images and roles as a centralized daemon for container management.
Runc is a low-level container runtime, as it directly uses namespace and cgroups to create containers.
In conclusion, the Docker engine architecture is composed of several components that work together to provide a powerful and efficient containerization platform. Understanding the architecture of the Docker engine is essential for developers who want to use Docker to build, deploy, and run containerized applications.
We don't have to dig deep too far unless we are in research over cloud-native, for understanding this much is enough.
Please subscribe to my newsletter and you can connect me through my social media handles.
Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/in/tarang-sharma-860808190/
Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYK2lzrujaV51DWsJ22rQRw#Docker #WeMakeDevs #kubernetes #Dok #devops